- Fancy Gold Jewellery
- Uttarakhandi Jewellery
- Silver Jewellery



GOLD GUIDE


YELLOW GOLD


The term 'gold' originates from the Old English word “geolu,” signifying yellow. Since ancient times, gold has captivated civilizations worldwide, cherished for its allure and aesthetic appeal. Its radiant hue frequently endowed it with significance in mythology and continues to be esteemed as a prized possession in contemporary times.

GOLD FACTS
- Approximately 49% of the global gold production is allocated to jewellery crafting, while the remaining portion serves industrial purposes. Despite the extraction of 187,200 tonnes of gold to date, an estimated 80% of the world's total gold reserves are yet to be unearthed.
- Despite gold's diverse colour palette, yellow remains the most favoured hue. Alloys are blended with 24 karat gold to enhance its durability, as its inherent malleability renders it exceedingly soft. This alloying process also facilitates colour alteration.
- While 24 karat gold stands as pure, malleable gold unfit for jewellery, 22 karat and 18 karat gold are predominantly utilized in India. In contrast, European and other nations commonly employ 14 karat, 10 karat, and even 9 karat gold.
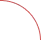
- Each jewellery piece bears stamps denoting its purity, hallmark logo, brand name, and jeweller's identification mark, facilitating future exchanges or sales for the customer and aiding the jeweller in product recognition.
- Hallmarking guarantees that a product is crafted with the precise karat weight claimed. Commonly used alloys for altering gold's caratage and colour include copper, nickel, silver, zinc, palladium, and manganese.
Karat Gold Content (Degree Of Purity) 24 Karat 99.95+% 22 Karat 91.6% 21 Karat 87.5% 20 Karat 83.3 18 Karat 75.0% 15 Karat 62.3% 14 Karat 58.5% 10 Karat 41.7% SHADES OF GOLD
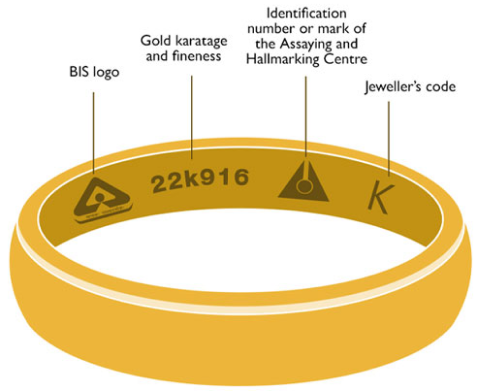
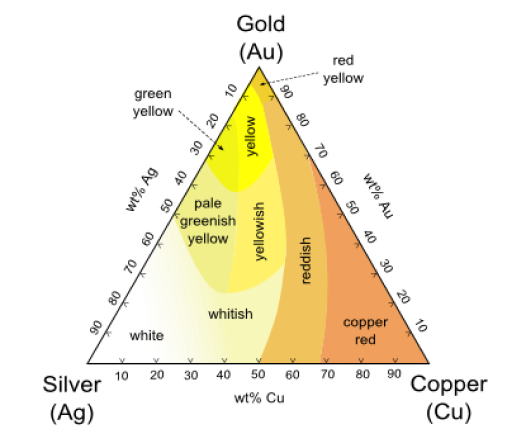
Gold of varying colors maintains the same purity and authenticity as its traditional yellow form. Since pure gold is too soft for jewelry, it is blended with alloys to enhance its durability. Each metal alloy imparts a distinct hue, resulting in shades ranging from white and pink to red and green. For instance, white gold incorporates nickel and silver, pink gold includes copper, and green gold utilizes silver. Additionally, the shades of yellow gold fluctuate depending on the alloys mixed for different karat weights. The accompanying illustration illustrates the diverse color spectrum of gold.
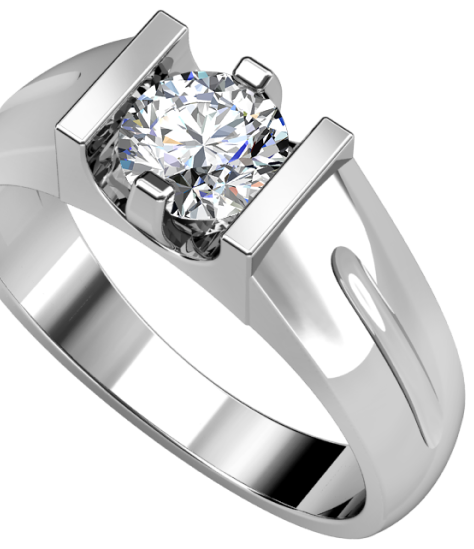

WHITE GOLD

White gold emerged into prominence during the 1920s, driven by the increasing preference for platinum in engagement rings. The surge in platinum's popularity led to a rising demand for white gold. Its affordability and similarity in appearance to platinum made it indistinguishable between the two metals. Although its significance waned over time, white gold experienced a resurgence in the 21st century, becoming the preferred choice for engagement and wedding rings.
GOLD FACTS
- White gold obtains its distinctive hue through a blend of alloys such as nickel, palladium, silver, and zinc with yellow gold. To maintain its white appearance, white gold must contain a minimum karat weight of 18k; beyond this threshold, its white coloration diminishes, often displaying a slight yellowish tint that necessitates a rhodium coating.
- Similar to yellow gold, the karat weight of white gold is gauged on the basis of gold content, with 18k signifying 75% gold content. The distinguishing factor lies in the coloration of the alloys utilized.
- Following yellow gold, white gold stands as the second most popular metal, particularly revered as the preferred choice for engagement rings across the globe.
- When set against white gold, diamonds ranging from colorless to light brown hues tend to exhibit greater visual appeal than those with yellowish tints, as the yellow undertone becomes distinctly noticeable against the white gold backdrop to the naked eye.
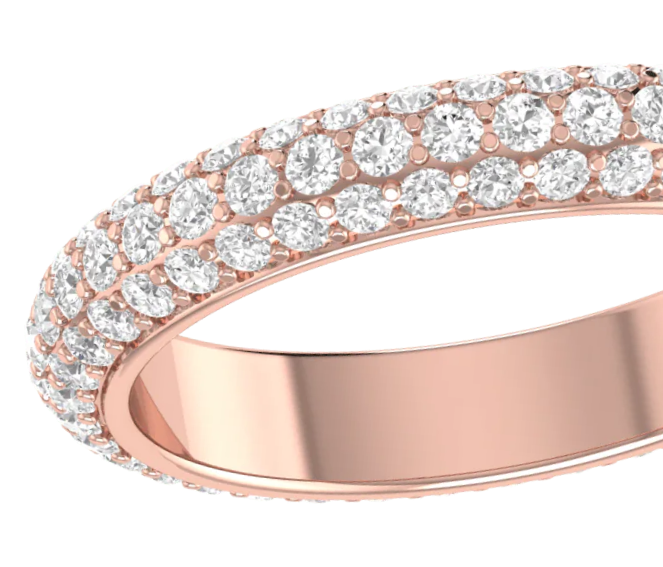

ROSE GOLD

Rose gold emerged into prominence during the 1920s, driven by the increasing preference for platinum in engagement rings. The surge in platinum's popularity led to a rising demand for white gold. Its affordability and similarity in appearance to platinum made it indistinguishable between the two metals. Although its significance waned over time, white gold experienced a resurgence in the 21st century, becoming the preferred choice for engagement and wedding rings.
ROSE GOLD FACTS
- Rose gold obtains its distinctive hue through a blend of alloys such as nickel, palladium, silver, and zinc with yellow gold. To maintain its white appearance, white gold must contain a minimum karat weight of 18k; beyond this threshold, its white coloration diminishes, often displaying a slight yellowish tint that necessitates a rhodium coating.
- Similar to yellow gold, the karat weight of white gold is gauged on the basis of gold content, with 18k signifying 75% gold content. The distinguishing factor lies in the coloration of the alloys utilized.
- Following yellow gold, white gold stands as the second most popular metal, particularly revered as the preferred choice for engagement rings across the globe.
- When set against white gold, diamonds ranging from colorless to light brown hues tend to exhibit greater visual appeal than those with yellowish tints, as the yellow undertone becomes distinctly noticeable against the white gold backdrop to the naked eye.
218K Red Gold 75% Gold and 25% Copper 18K Red Gold 975% Gold, 22.5% Copper and 2.5% Silver 18K Red Gold 75% Gold, 20% Copper and 5% Silver Material 18k Yellow Gold 18k White Gold 18k Rose Gold % Gold 75% 75% 75% % Silver 10-20% 18.50% 2.75% % Copper 5-15% 1% 25.25% % Zinc 0% 5.50% 0% Please provide all your details
 WELCOME TOBATTULAAL
WELCOME TOBATTULAAL
 One-Time Password Verification
One-Time Password Verification Just enter the 6-digit code we sent you!
Just enter the 6-digit code we sent you!+91
Didn’t Receive the Code?
 Resend Code
Resend Code

Sign Up

BOOK AN APPOINTMENTs
 1User Details2Booking Details
1User Details2Booking Details1,945,396
Happy customers & counting!

Get me updated, with PRICE-DROP Alert!


FOR CHOOSING US

Item Added To Your Cart
- Uttarakhandi Jewellery



